Kubernetes v1.35 Upgrade Impacts
Today, let’s explore Kubernetes v1.35 upgrade. What’s New in Kubernetes, What Changed, and Why You Should Upgrade this v1.35.
Introduction
Kubernetes v1.35 delivers a high‑impact set of improvements across resource efficiency, scheduling intelligence, security, and platform hygiene. Compared to v1.34, this release turns several long‑running efforts (like in‑place Pod resize) into production‑ready features, adds smarter scheduling for AI/batch workloads, and continues tightening security and deprecating legacy tech such as cgroup v1.
Explanation of each Feature and Upgrade Impact
Let’s explore one by one each feature and Key changes
1. In‑Place Pod Resize – Now Stable Before in v1.34
- In‑place Pod resize existed but was not yet Stable; it required feature gates and was not broadly recommended for mission‑critical production.
- Many teams still relied on the classic pattern: change Pod resources → rollout new Pod → pay restart/cold‑start costs, which is painful for stateful and latency‑sensitive apps.
The Problem: Resource changes required Pod recreation with downtime
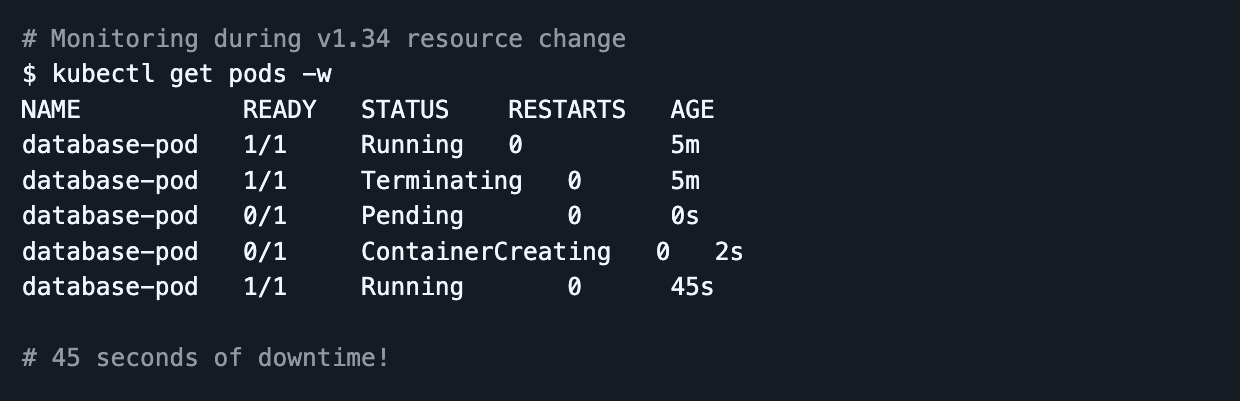
Now in v1.35
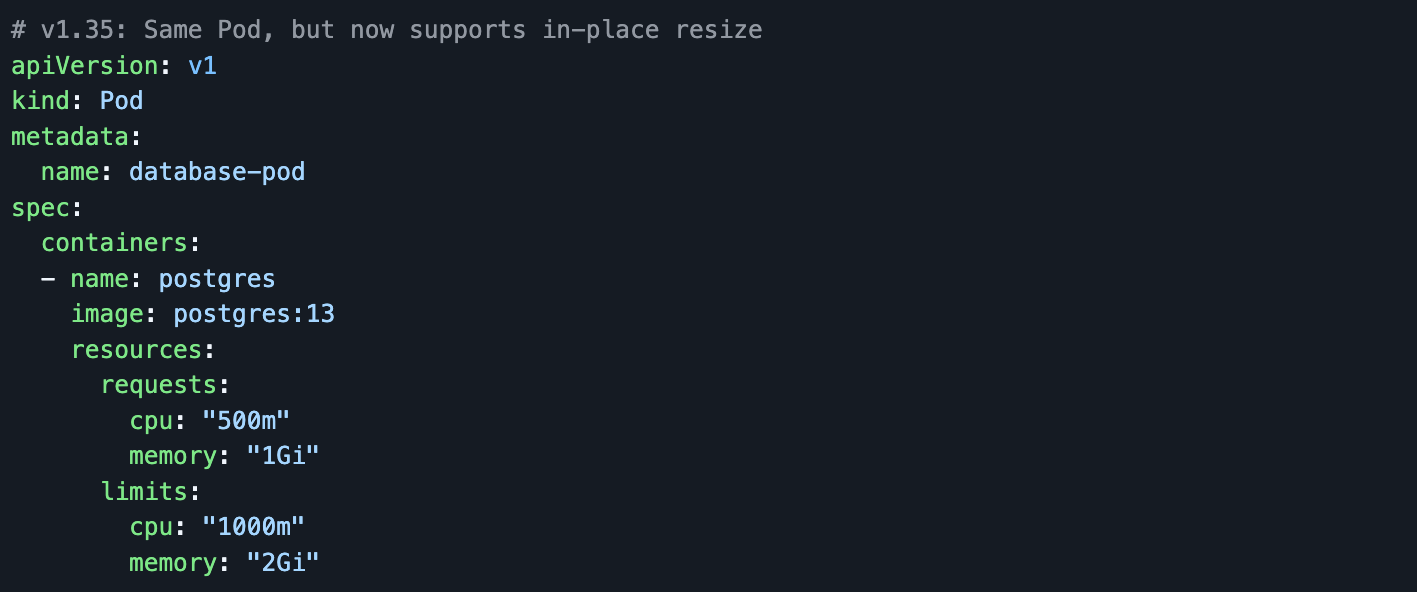
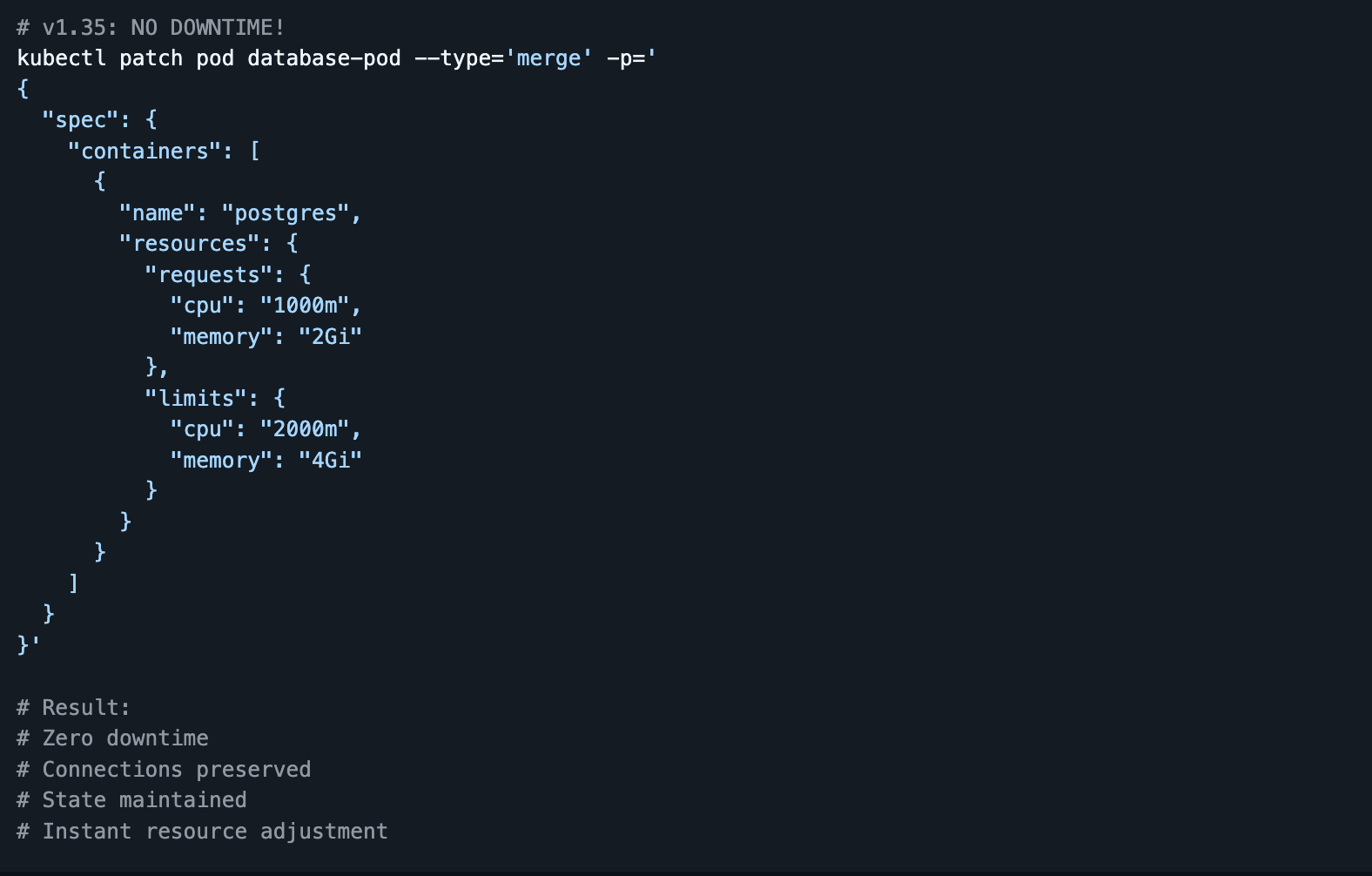
In‑place Pod resize is Stable (GA) and enabled by default. You can update CPU and memory for containers in a running Pod via the resize subresource without recreating the Pod.
Impact & Key Changes:
No restart tax: Scale up/down running Pods (for example, ML inference or Java services) without restarting them, avoiding cold starts and state re‑initialization.
Smarter tuning: Temporarily boost CPU/memory during heavy phases (startup, batch window) and shrink afterward to reduce waste.
Production‑ready vertical scaling: GA status means the feature is now supported for production use, with better ecosystem support in autoscalers and optimization tools.
Use Cases:
- Dynamic scaling for stateful applications
- Cost optimization without service interruption
- Performance tuning for long-running processes
The Solution: Zero-downtime in-place resource updates
2.
Workload‑Aware / Gang Scheduling for AI & Batch
Before in v1.34
Standard Kubernetes scheduling treated Pods largely independently; coordinating the all‑or‑nothing start of large AI or batch jobs required custom operators or external schedulers.
This made it harder to ensure that all replicas in a distributed training job could start together with the right resources, reducing efficiency and predictability.
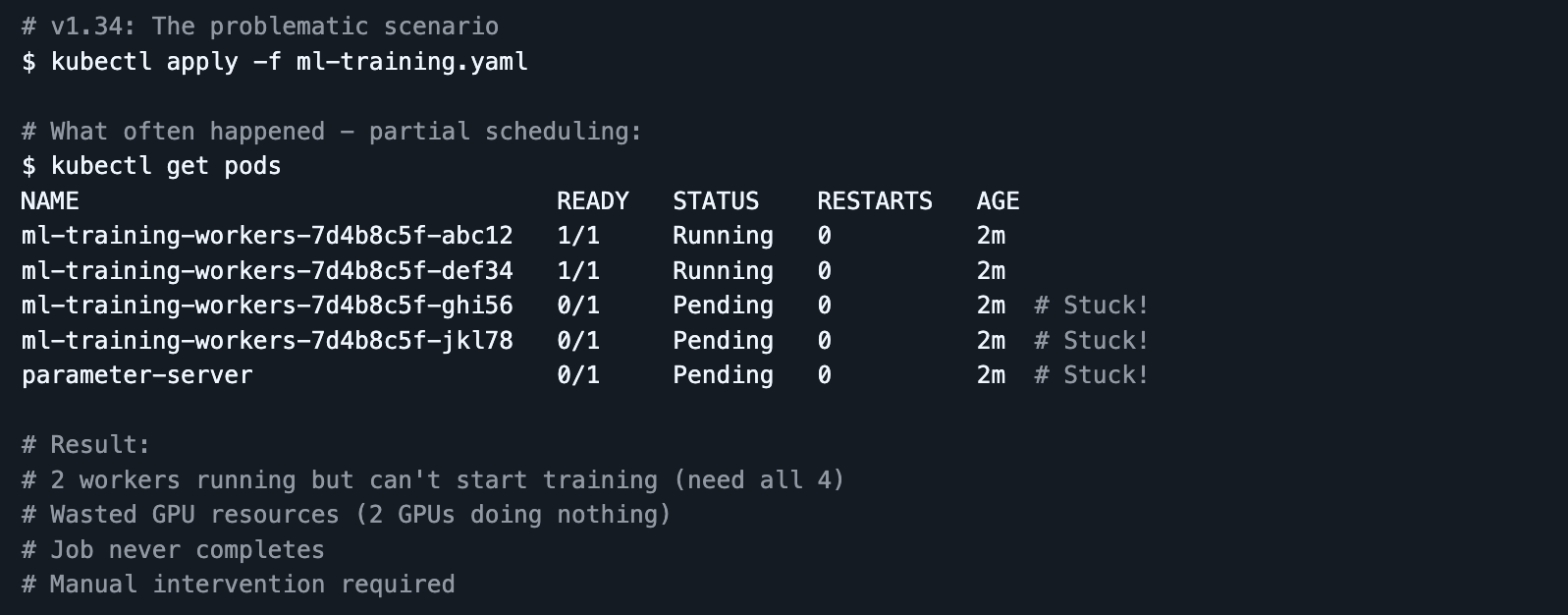
The Problem: Partial scheduling caused resource deadlocks
Now in v1.35
v1.35 introduces Workload‑Aware Scheduling and improvements around gang / batch scheduling semantics as alpha features, allowing schedulers to treat related Pods as a unit and reason about their collective resource needs.
The Solution: All-or-nothing gang scheduling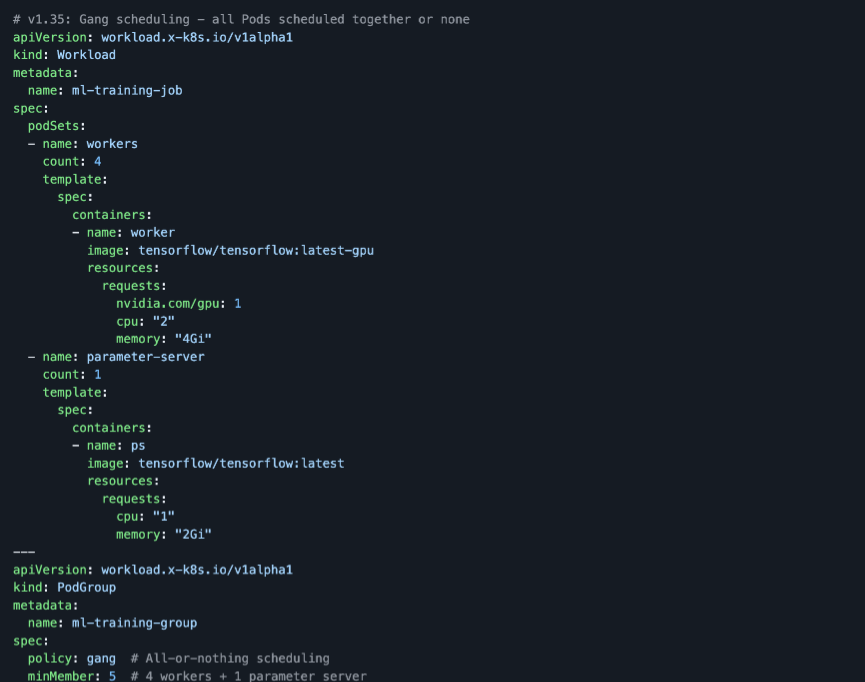
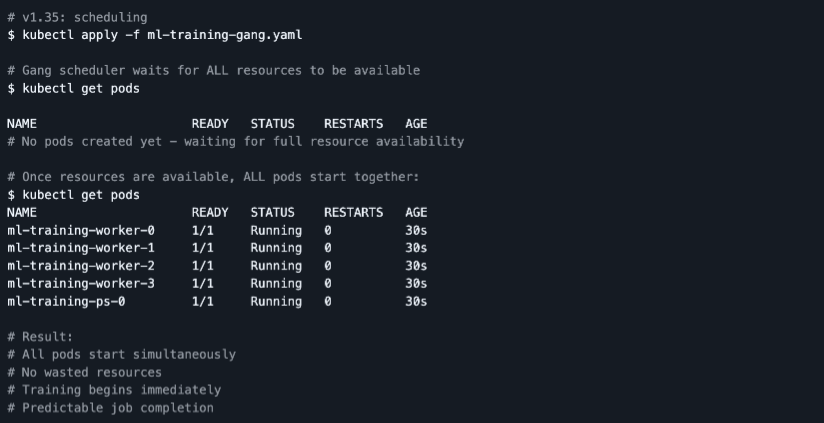 Impact & Key Changes:
Impact & Key Changes:
- Better AI/ML job starts: Distributed training or HPC jobs can be scheduled more reliably, only starting when all required Pods can get resources together.
- Reduced wasted capacity: Avoids situations where a subset of Pods lands without enough peers, sitting idle and wasting CPU/GPU time.
- Foundation for advanced schedulers: Provides primitives for more sophisticated, workload‑aware scheduling controllers that target AI, analytics, and large batch pipelines.
3. Traffic Locality & PreferSameNode (Service Hints)
Before in v1.34
- Service traffic routing was largely unaware of per‑Pod locality preferences beyond existing topology hints and external load‑balancer behaviors.
- For some latency‑sensitive services, keeping traffic on the same node or tightly scoped topology required custom routing logic or sidecars.
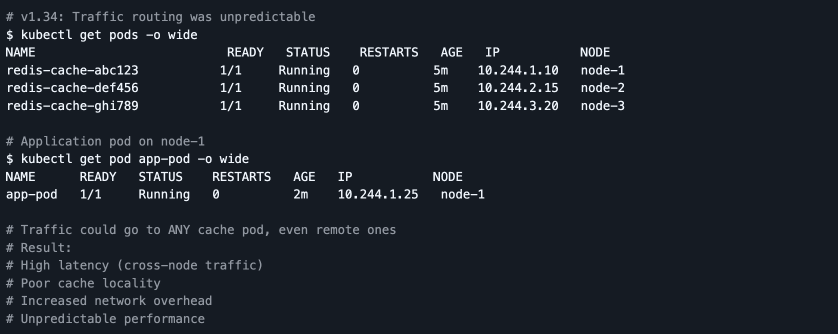
The Problem: No control over traffic locality
 Now in v1.35
Now in v1.35
v1.35 adds enhancements around workload‑aware and topology‑aware routing, including options that make it easier to prefer traffic staying on the same node when appropriate.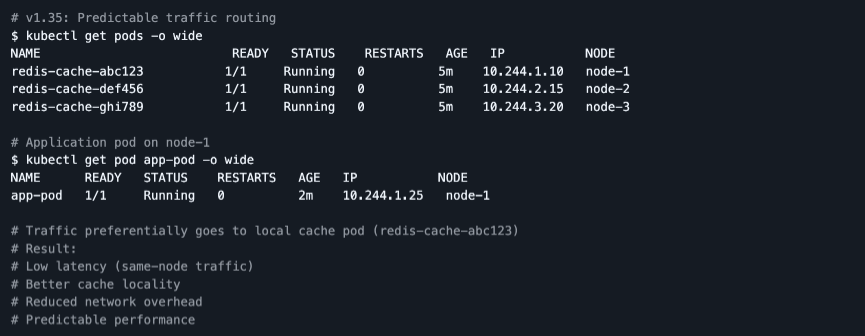
Impact & Key Changes:
- Lower latency for local calls: Requests can be kept closer to where Pods run, reducing cross‑node hops.
- Better cache locality: Local traffic helps cache‑heavy workloads (e.g., inference caches, sidecar proxies) reuse warm data.
- More predictable performance: Topology‑aware routing provides more consistent latency characteristics, especially in multi‑zone or edge‑like setups.
---
5. Pod Certificates for Workload Identity
Happy Learning!